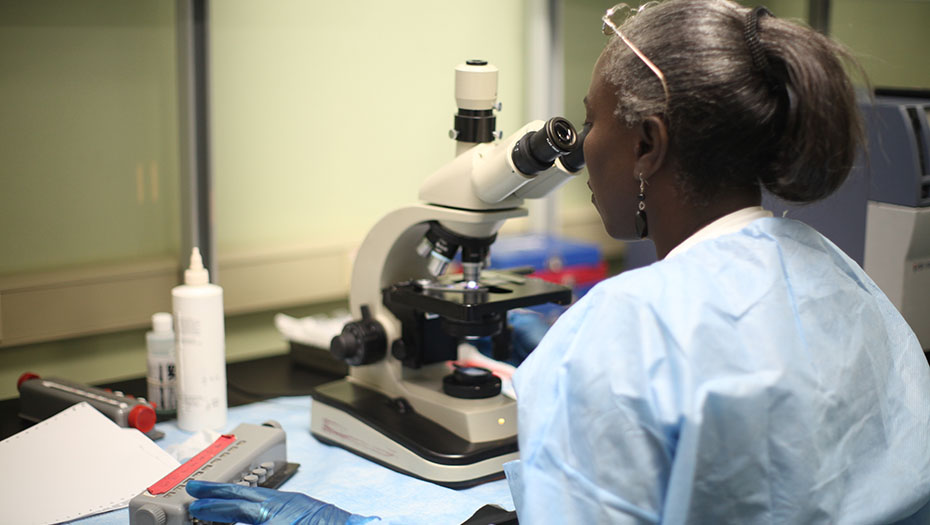
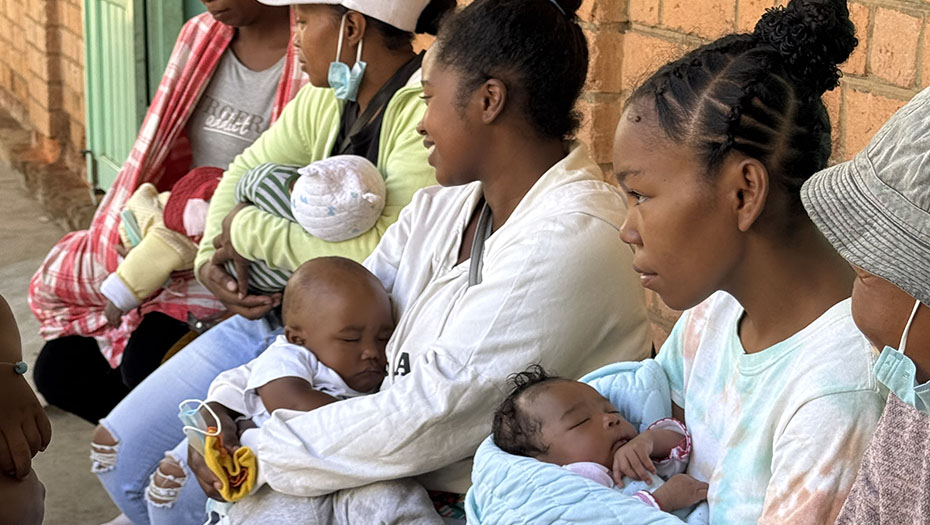
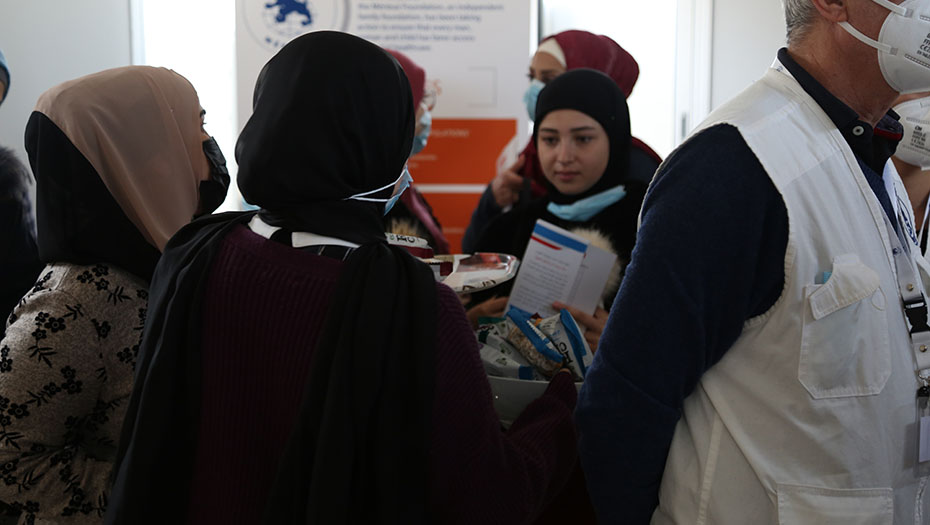
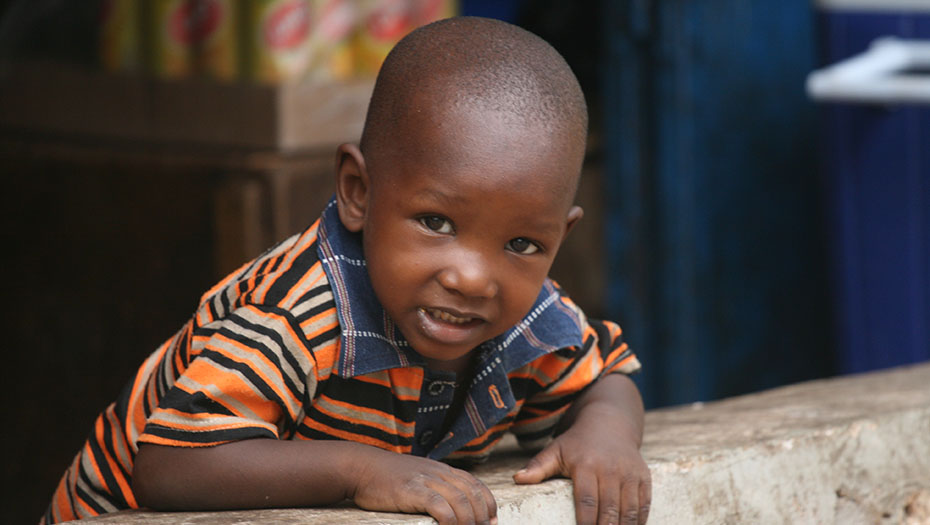
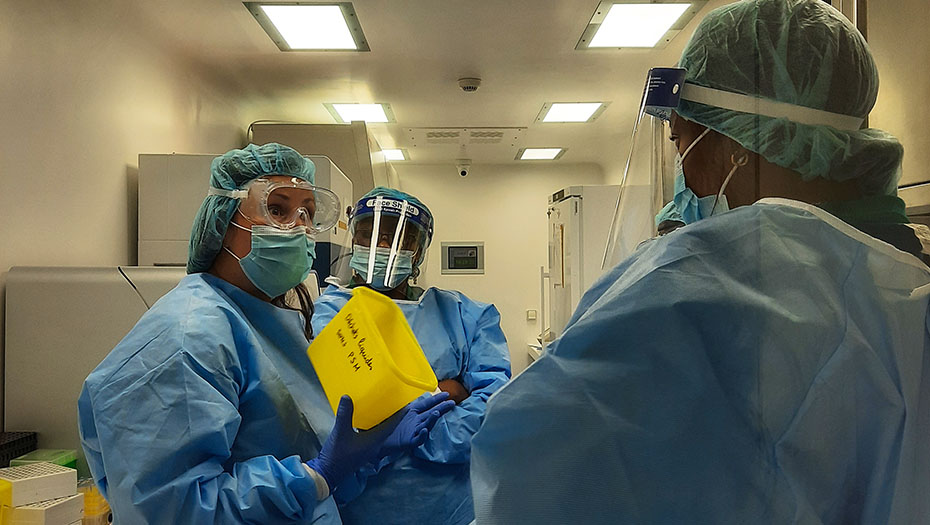
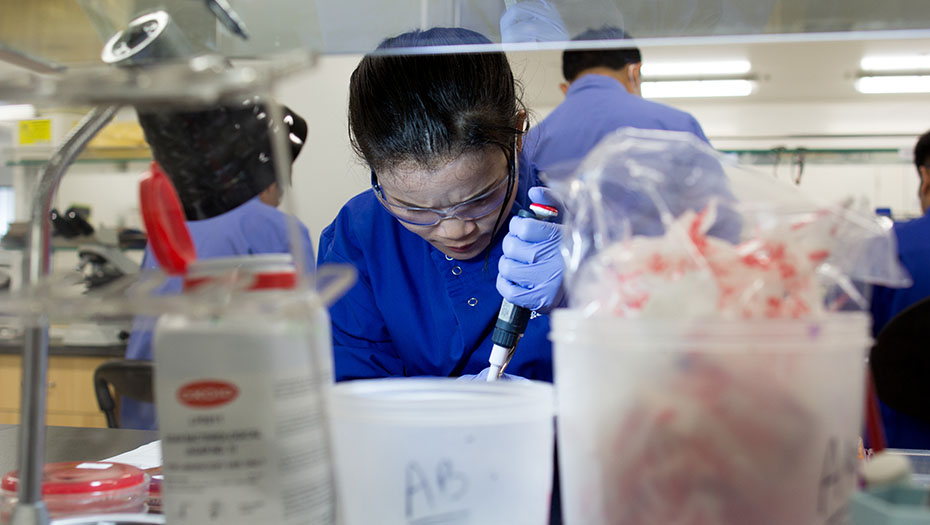
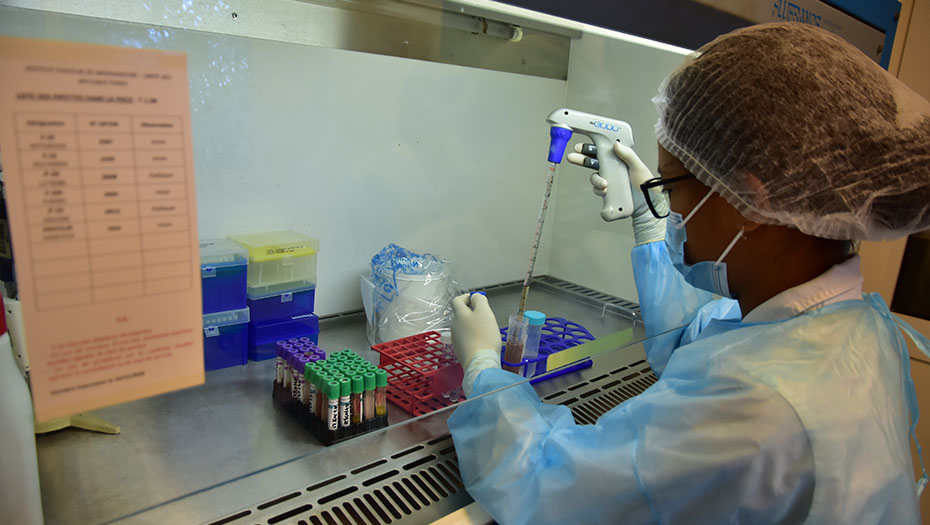
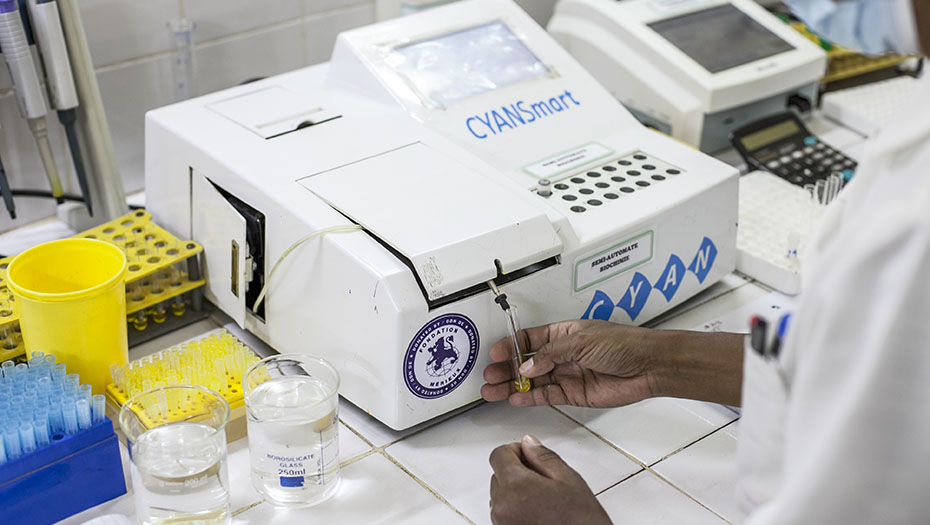
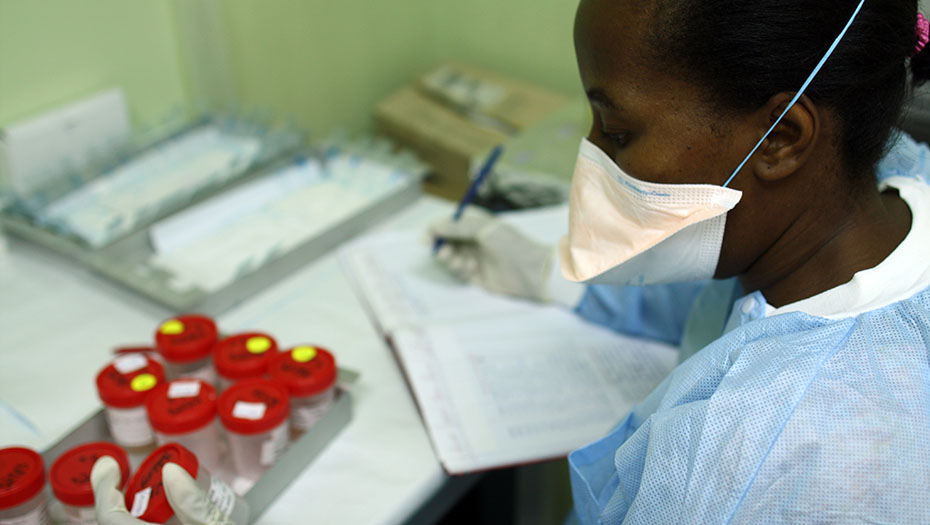
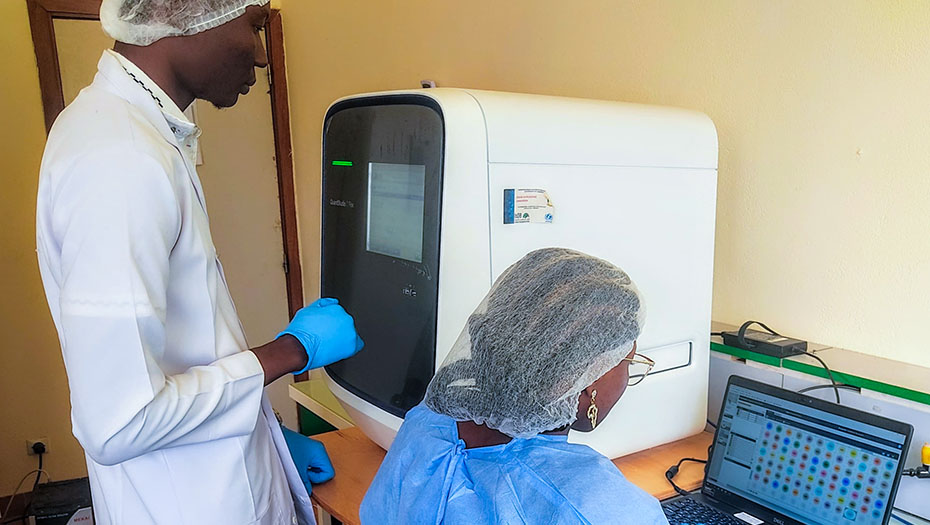
By strengthening laboratory structures and supporting health authorities in the construction of efficient laboratory systems, the Mérieux Foundation helps to improve the care of the most fragile populations and optimize health surveillance, including resistance to antibiotics.
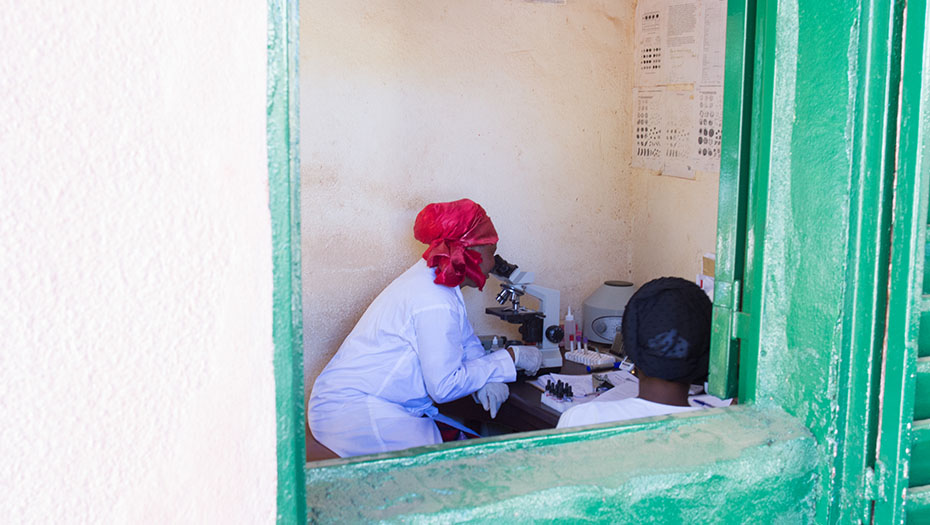

The Mérieux Foundation supports the establishment of high-level biomedical laboratories through collaborations with national and international private and public organizations. In an increasingly complex world in which conflicts, epidemics, and population displacements are becoming more commonplace, the Foundation has established a reputation for its expertise in biology and infectious diseases. It makes an active contribution to tackling infectious diseases and is one of the organizations approved by the Global Fund as a technical laboratory expert.
This expertise is based on four main cornerstones:
- Modernization of infrastructure and equipment
- Strengthening the skills and expertise of laboratory staff
- Sustainability of structures
- Establishment of networks and laboratory systems
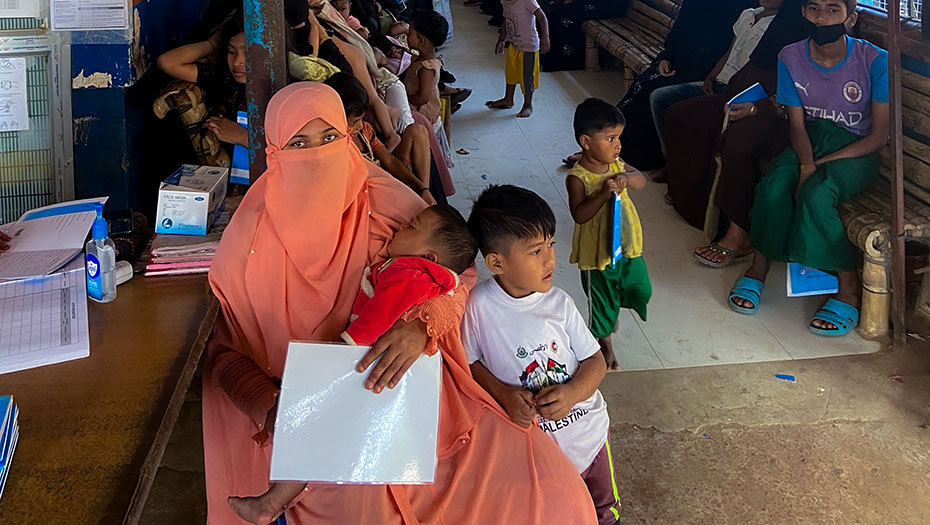
2024 was marked by significant challenges in terms of security and the geopolitical situation in several of the areas in which the Foundation operates, in particular in Lebanon, Haiti, and Bangladesh. In West Africa, the diplomatic context is making it difficult to continue or launch projects. In this changing environment, our beneficiaries and partners can count on the commitment, flexibility, and adaptability of our teams and our network of institutional partners.
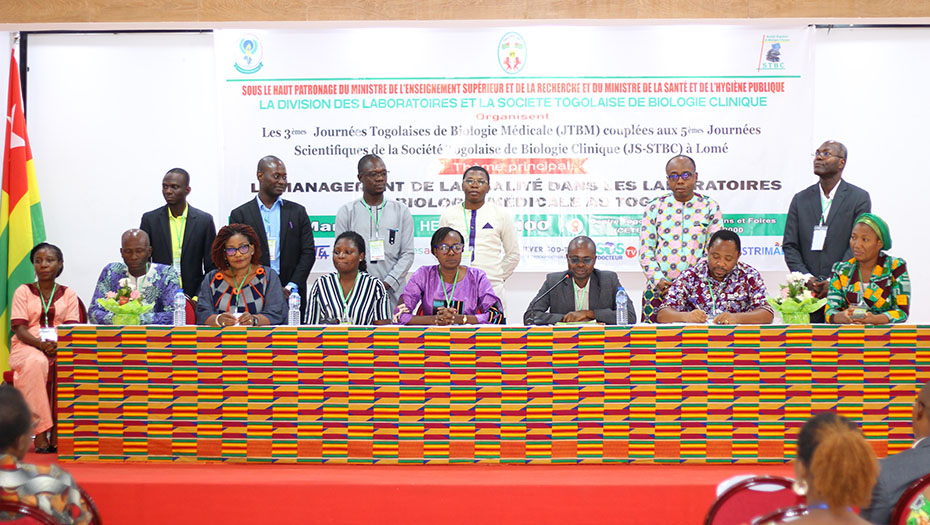
In 2024, the Mérieux Foundation’s expertise in reinforcing clinical biology laboratories was deployed across more than 40 projects in more than 20 countries.
- Virology expertise
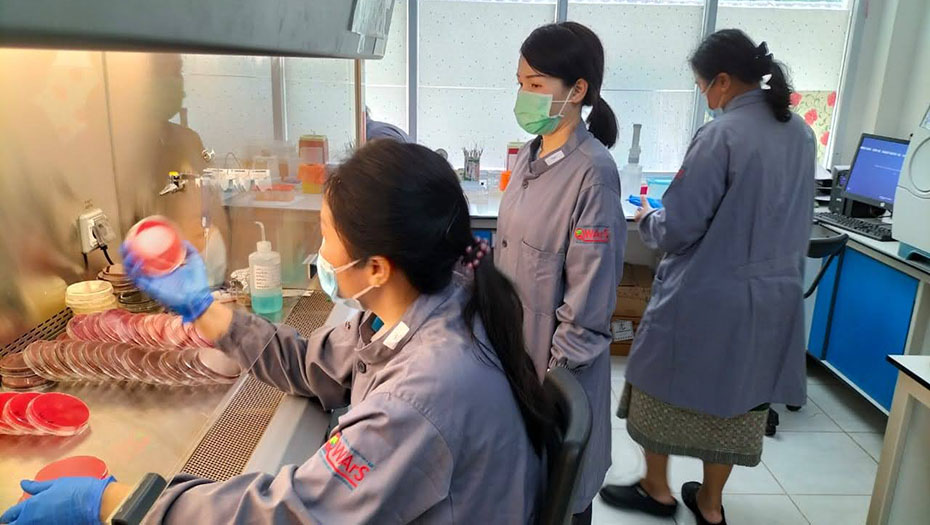
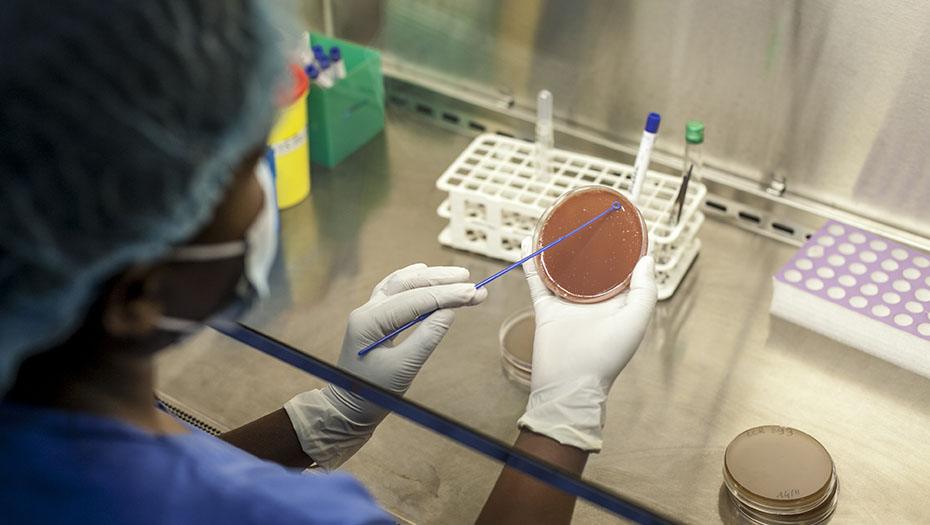
- Bacteriology expertise
- Educational engineering expertise
- Infrastructure expertise
- Quality management system expertise
- Biosafety and biosecurity expertise
- Laboratory IT systems expertise
- Expertise in health surveillance based on laboratories
- Expertise in laboratory development policies